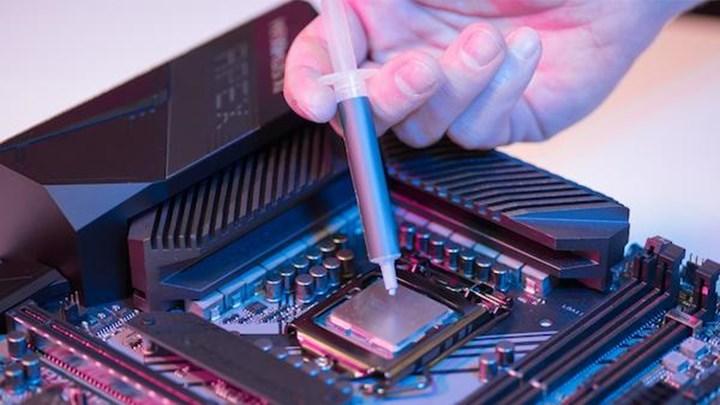

Especially in hot weather, the preferred cooling solution is as important as the CPU cooler. The overheating problem brings with it the performance problem. So what is the best solution for CPU cooling?
In order for the processor to work as efficiently as possible, it is necessary to find the best cooling solution. Since the processor generates heat while performing tasks, heat build-up can cause overheating, causing performance issues. That’s why you need the best CPU cooling solution to avoid overheating. This is a must if you plan to overclock your hardware. When it comes to CPU cooling, you have two basic solutions: Thermal paste or Liquid metal. So, what is the best solution for cooling the processor? What is the difference between thermal paste and liquid metal?
Preferring liquid metal for CPU cooling
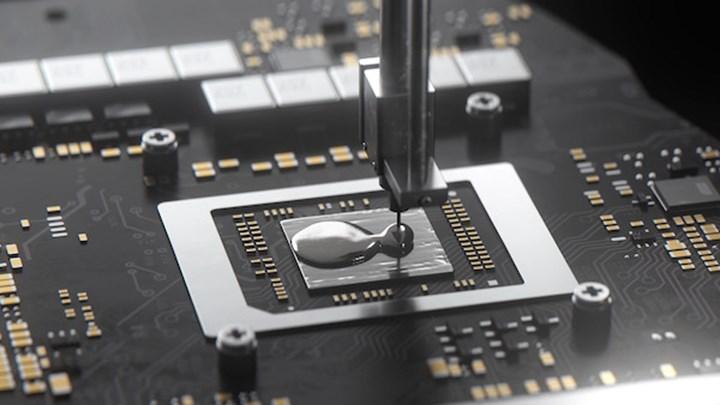
The main component of the liquid metal thermal interface material is gallium. The liquid metal works by minimizing microscopic air gaps between your processor’s built-in heat spreader and the heat sink’s cold plate. Because air is a poor conductor of heat, filling these microscopic air gaps paves the way for efficient heat transfer from the processor to the heat sink; thus keeping your processor cool at all times. As you know, liquid metal is almost always electrically conductive. This means it can carry current from one point to another.
Liquid metal advantages
The biggest advantage of liquid metal over thermal paste is thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of liquid metal dissipates heat from your processor faster than thermal paste. The best liquid metal has a thermal conductivity rating of more than 73W per kelvin.
Liquid metal disadvantages
However, liquid metal has two major disadvantages. First, it is difficult to apply as it requires more precautions than the commonly used thermal paste. A single drop outside of the target area can cause certain components to fail if you clear the short circuit when you power up your hardware. Also, since the main element is gallium, the liquid metal can react chemically with aluminum. Therefore, if your CPU cooler has an aluminum cold plate, you should not use it. Second, liquid metal is more expensive than regular thermal paste due to its higher thermal conductivity rates.
Choosing thermal paste for CPU cooling
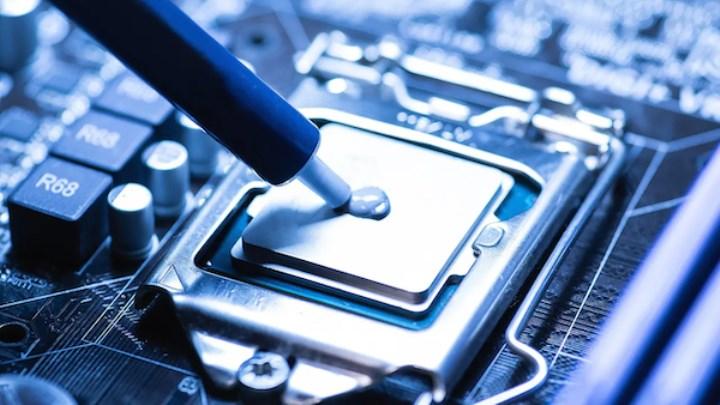

Thermal paste, sometimes called thermal grease or thermal compound, is another cooling option for your PC. Unlike liquid metal, it is not electrically conductive. But thermal paste and liquid metal have the same working mechanism. There are different types of thermal paste based on the type of compound used, including metal-based, silicone-based, and ceramic-based pastes.
Thermal paste advantages
Thermal paste is quite popular; there is good reason for this. One of the most important reasons is that it is easy to apply. Since it is not electrically conductive, it does not affect the structure of your computer even if you carry it. You can apply and reapply the thermal paste as you wish. Thermal paste is also suitable for those on a budget, it is a cheaper processor cooling option.
Thermal paste disadvantages
Thermal paste is more affordable, but its biggest drawback is its thermal conductivity. Thermal conductivity of thermal paste has no chance compared to liquid metal. Some of the best thermal pastes have thermal conductivity of just over 15w/mk, which is far less than what you get with liquid metal.
Thermal paste or Liquid metal?
The answer varies. Liquid metal has a higher thermal conductivity, but has significant risks in practice. That’s why liquid metal is best for those who know what they’re doing. Thermal paste, on the other hand, is cheaper, but you have to make do with lower degrees of thermal conductivity. Thermal paste is easy to apply and does not pose many of the risks of using liquid metal. It’s pretty manageable with thermal paste, but if you need better cooling than the average user and are prepared to deal with the risks, you can opt for liquid metal.