 The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) announced the contents of the sample collected from the asteroid after the OSIRIS-REx capsule returned to Earth with great fanfare late last month. After the OSIRIS-REx mission was launched in 2016, it flew to the asteroid Bennu and collected samples from the celestial body. The findings obtained as a result of the seven-year mission point to carbon and water.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) announced the contents of the sample collected from the asteroid after the OSIRIS-REx capsule returned to Earth with great fanfare late last month. After the OSIRIS-REx mission was launched in 2016, it flew to the asteroid Bennu and collected samples from the celestial body. The findings obtained as a result of the seven-year mission point to carbon and water.A historic success
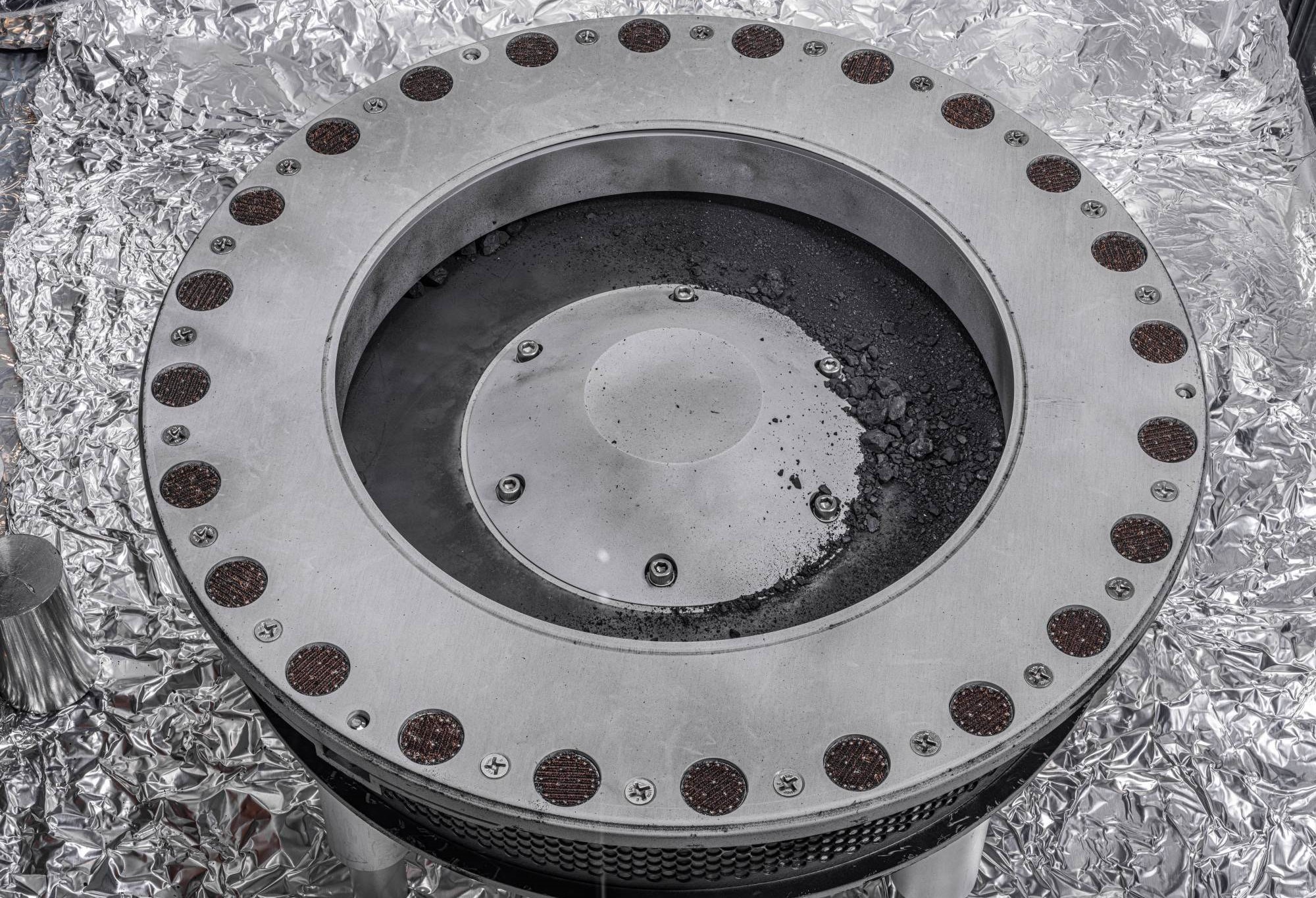
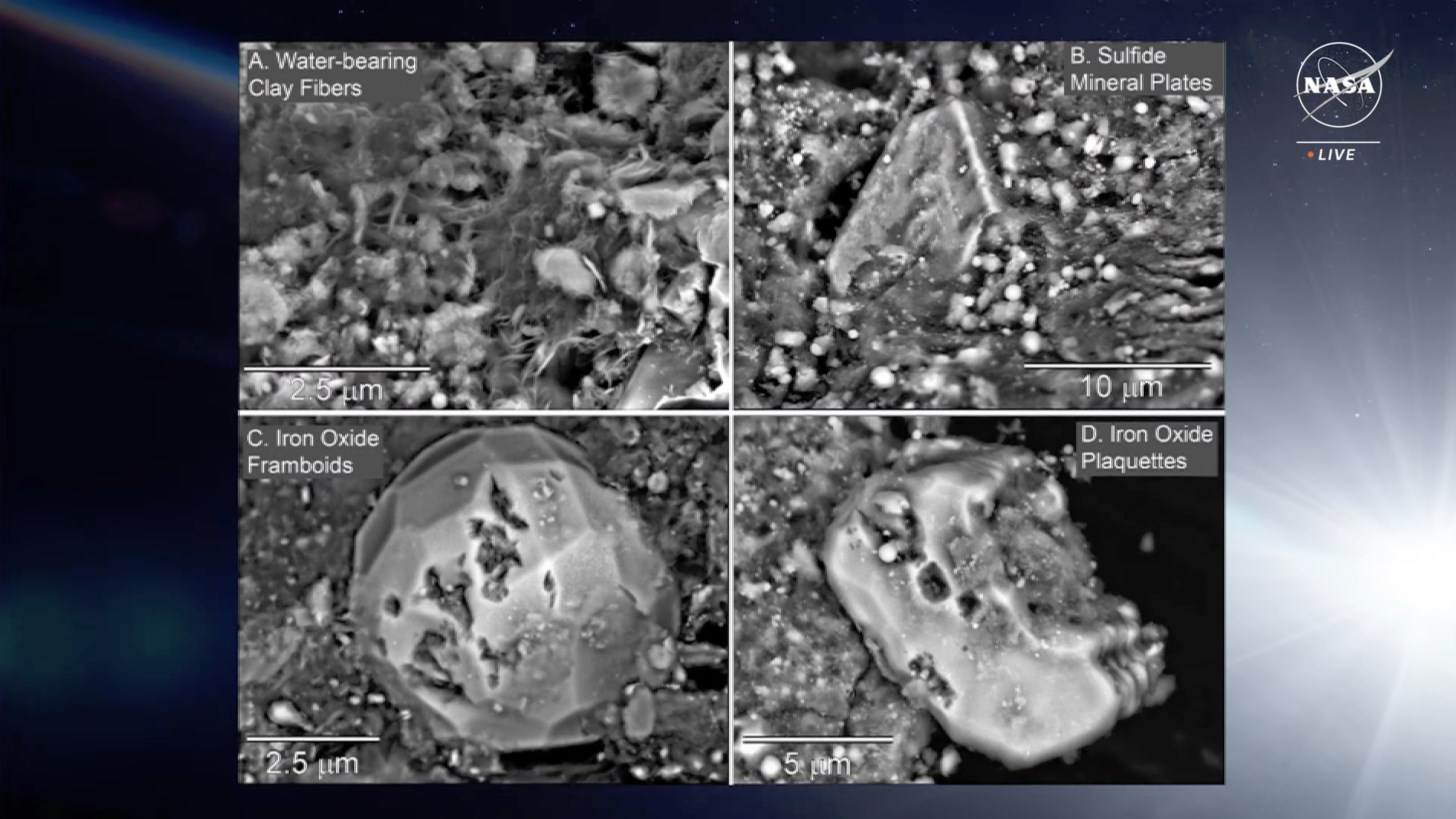 The mission, called OSIRIS-REx, delivered pieces of the 500-meter-wide Bennu to Earth late last month. NASA provided the first look at the sample during a live broadcast and also offered a summary of the first analyzes of material beyond Earth. Mission team members stated that these initial scientific results are promising and that Bennu is rich in both water and carbon-containing compounds.
The mission, called OSIRIS-REx, delivered pieces of the 500-meter-wide Bennu to Earth late last month. NASA provided the first look at the sample during a live broadcast and also offered a summary of the first analyzes of material beyond Earth. Mission team members stated that these initial scientific results are promising and that Bennu is rich in both water and carbon-containing compounds.“NASA missions like OSIRIS-REx will improve our understanding of asteroids that could threaten Earth while also giving us a glimpse of what lies beyond,” NASA Administrator Bill Nelson said in a statement. “The sample made it back to Earth, but there is still a lot of scientific work to be done – work like we have never seen before.” he said.
How was it?
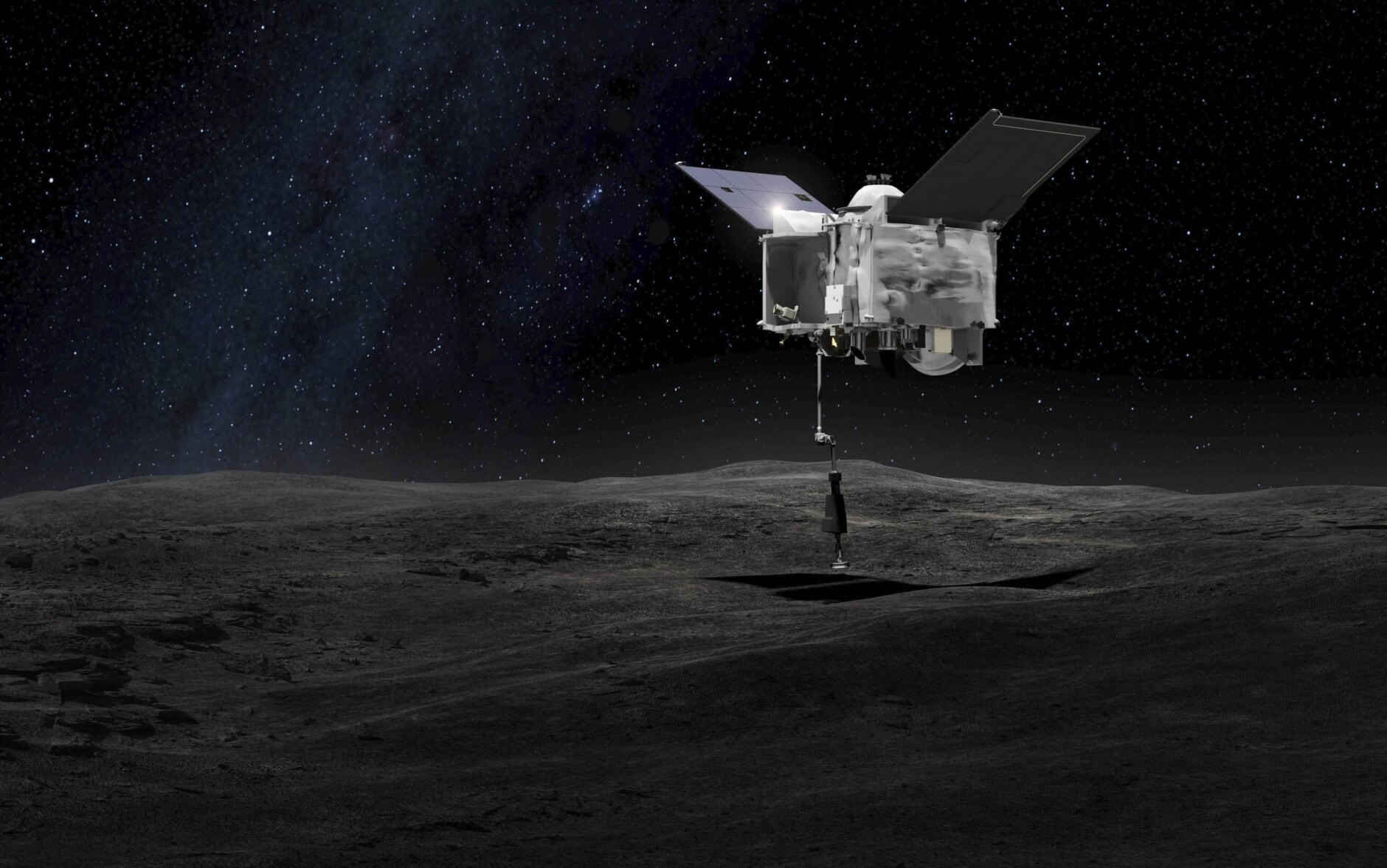 OSIRIS-REx was launched in September 2016 and arrived at Bennu in December 2018. The probe spent the next 22 months studying the space rock from orbit and searching for the right place to go down and collect a sample. This sampling effort took place in October 2020 and revealed something quite dramatic: Bennu’s surface was surprisingly porous and soft.
OSIRIS-REx was launched in September 2016 and arrived at Bennu in December 2018. The probe spent the next 22 months studying the space rock from orbit and searching for the right place to go down and collect a sample. This sampling effort took place in October 2020 and revealed something quite dramatic: Bennu’s surface was surprisingly porous and soft.Although this situation misled the predictions, OSIRIS-REx managed to collect much more material than thought. Afterwards, OSIRIS-REx set out for Earth in May 2021. The journey home was completed on September 24, when OSIRIS-REx’s return capsule touched down in the northern Utah desert.
What will happen now?
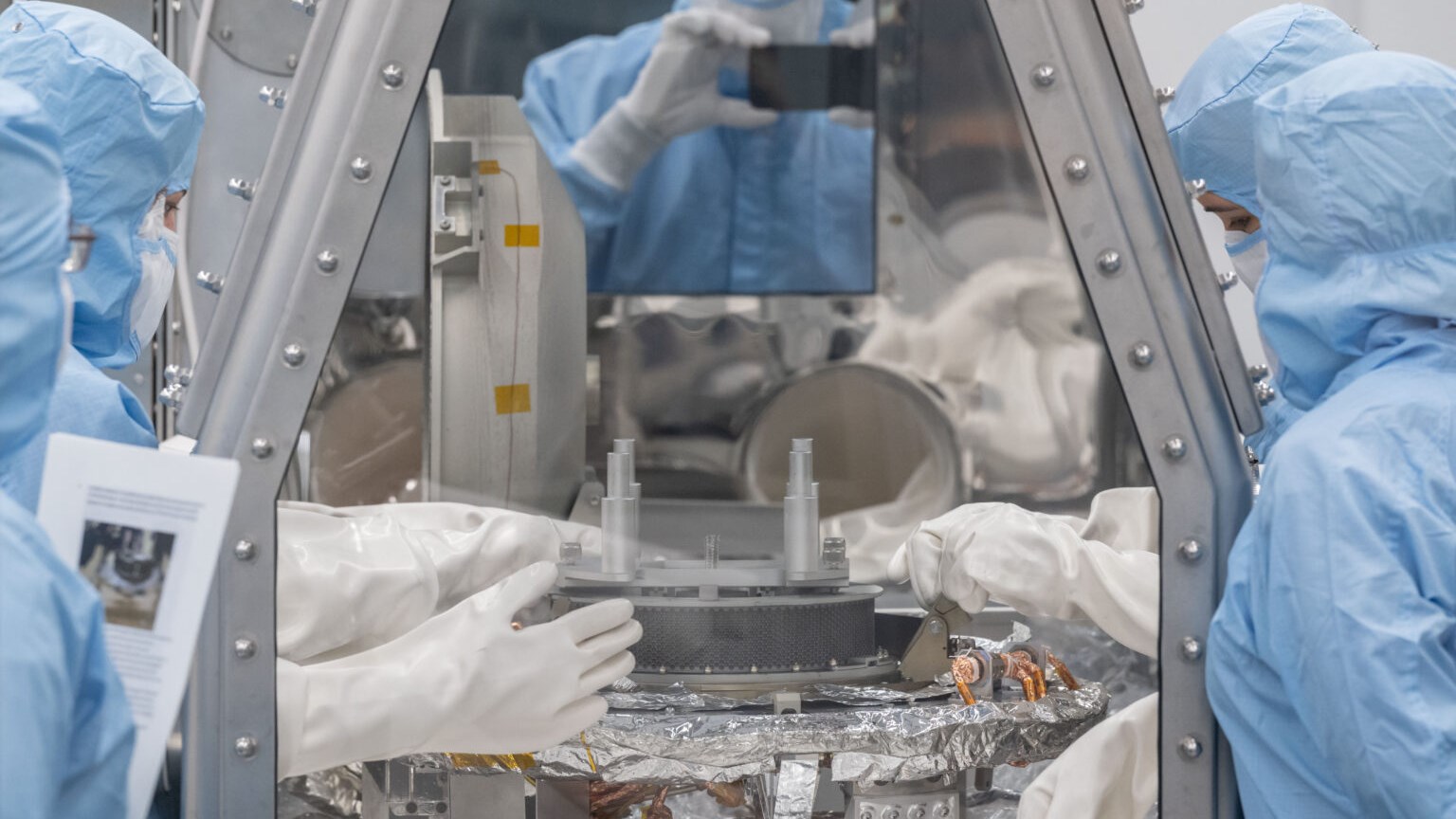 It should be clearly stated that this adaptation has only just begun. For example, mission team members still don’t know exactly how much material OSIRIS-REx is carrying home. It is thought to weigh around 250 grams (it was targeted to be 60 grams), but this is only an estimate calculated while the return capsule was still in space.
It should be clearly stated that this adaptation has only just begun. For example, mission team members still don’t know exactly how much material OSIRIS-REx is carrying home. It is thought to weigh around 250 grams (it was targeted to be 60 grams), but this is only an estimate calculated while the return capsule was still in space.The asteroid sample, now at NASA’s Johnson Space Center (JSC) in Houston, will be distributed to researchers around the world over the coming months and years, and these samples will be studied in detail in a global study. The researchers’ work will, among other things, examine the identity of carbon compounds that could shed light on how life began on Earth. Many researchers think that carbon-rich asteroids like Bennu hit our planet long ago and formed the building blocks of life.
Mission team members state that Bennu belongs to the early periods of our Solar system (and is therefore 4.5 billion years old), so a full understanding of the samples is extremely important. “The abundance of carbon-rich material and abundance of water-bearing clay minerals are just the tip of the cosmic iceberg,” said OSIRIS-REx principal investigator Dante Lauretta.
Meanwhile, the journey is not over yet for the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Although the return capsule has now returned to Earth, the probe continues to fly towards another asteroid called Apophis. OSIRIS-REx is planned to reach this space rock in 2029 and examine it closely with an extended mission called OSIRIS-APEX.