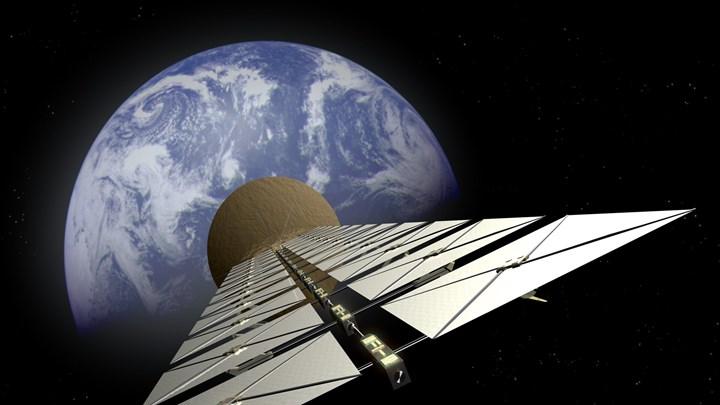

The need for energy for countries and giant companies around the world has never been more important. In this context, the European Space Agency (ESA) revealed that it is looking for alternative ways to solve the problem. The agency’s plans include meeting its energy needs through space-based solar energy systems.
“It will be up to Europe, the ESA and its member states to push the boundaries of technology to solve one of the most pressing problems of this generation for people around the world,” said Josef Aschbacher, head of ESA. Some time ago, ESA worked with UK and Germany-based consulting groups to identify the costs and benefits of space-based solar development. The results of this study were published on ESA’s website to inform policy makers.
World’s largest heat pump to be built in Germany
ESA’s solar energy project from space is being launched as the Solaris Program. This program will be presented to the ESA Council, which will be held at ministerial level in November, and funding will be determined for the project. However, according to Aschbacher’s plans, the development of the solar energy system will begin in 2025.
Solaris project costs too high
Within the scope of the project, it is stated that one-third of Europe’s annual electricity consumption, which is at the level of 3,000 TWh, can be met, and it is stated that the development and commissioning of the necessary systems will cost hundreds of billions of euros.
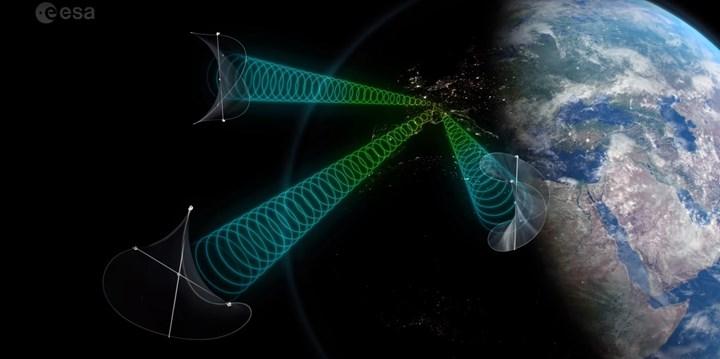
The project requires the establishment of a giant satellite constellation 36,000 km from the earth. For comparison, the system, which is planned to be exactly 10 times the mass of the ISS, will require hundreds or even thousands of launches. Therefore, reusable rocket systems such as SpaceX’s Falcon are critical. They also require an increase in their lifting capacity, as is the case with the Falcon Heavy. According to the research, if the current lifting capacity increases by 200 times, satellites can be placed into orbit in 4 to 6 years.
How does space-based solar power work?
Conceptually, space-based solar power is pretty simple. Satellites orbiting well above the Earth’s atmosphere continuously collect solar energy and convert it into current. This energy is then sent back to earth via microwaves. The energy captured by photovoltaic cells or antennas is converted into electricity for use in housing and industry. The biggest benefits of collecting solar energy from space are the absence of night, clouds or seasonal factors that interfere with the collection.
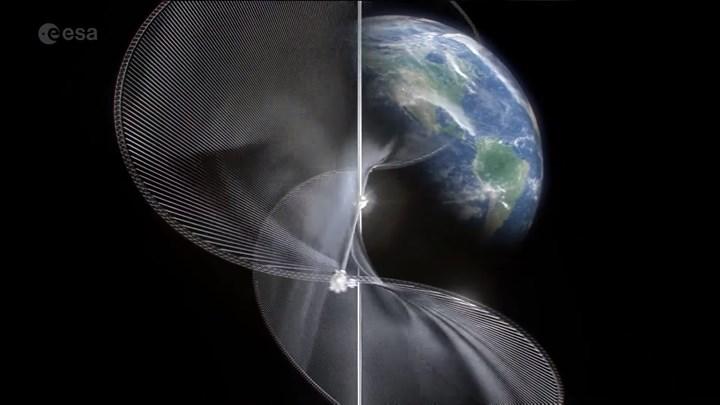
The project has disadvantages
As you know, there is a name who is interested in both space and solar energy: Elon Musk. A few years ago, Musk said about getting solar power from space, “This is the dumbest thing ever.” According to Musk, the efficiency of this process is a question mark. Yes, a lot more solar energy can be obtained with an orbiting solar panel, but it has to be converted twice to turn it into electricity on earth: from photon to electron, then back to photon. Conversion efficiency plays a key role here. Therefore, let us underline that there are great obstacles in front of this project.