Crypto holders can house their assets under exchange custody, non-custodial or profit-making custody. So which of these makes sense?
The development of the crypto industry ensures that more and more crypto participants appear regularly. However, crypto participants are thoughtful about which crypto wallet to store their acquired crypto assets.
What are the other wallet models that attract attention with the working logic of crypto wallets, the structure of exchange wallets and alternative structures?
Crypto Wallets and Featured Details
People who want to enter the crypto industry may be wondering where and how they should keep their assets. The prominent details in crypto wallets are important for hosting assets. On the other hand, users who hold crypto assets carefully examine their asset valuation models.
1- Profitable Wallets
Another trend of crypto users is wallet models that provide profit. Here, users can take profits on the table while keeping their crypto assets. In this wallet model, passive interest opportunities can be one of the prominent details. Platforms such as VestUp can be cited as an example for this model with the benefits they offer to their users hosting their assets.
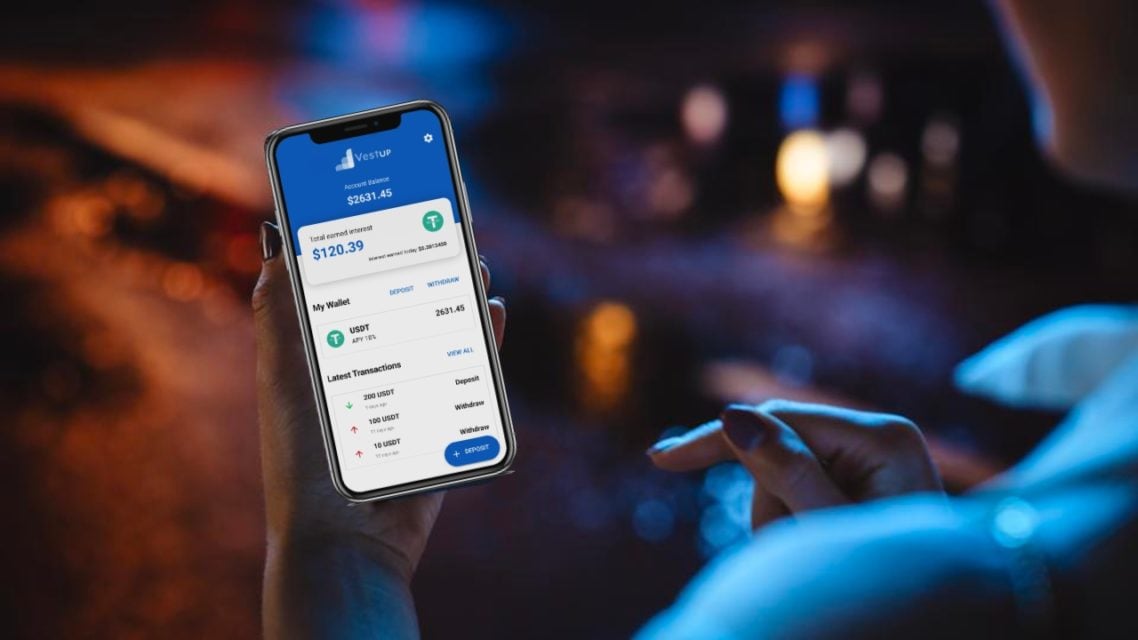
This feature, which is limited in centralized exchanges, is a positive feature of profit-making wallets. This wallet model also provides its users with more efficient service with the security measures it offers against fraud.
2- Custodial (Wallets under Custody)
Three different crypto wallet models stand out that users can evaluate. One of them is the most notable part of the list as the surveillance of assets. Because these wallet models generally use the stock market infrastructure. Exchange wallets, which have a custodial (third party custody and custody) structure, keep users’ assets as escrow.
Assets held here do not offer profits to users if no staking is done. In case of stock market bankruptcies such as FTX, it has been seen that these wallets and the users with assets may be in danger. FTX victims still haven’t managed to get their assets. The recoverability of the wallet is directly related to the completion of the legal processes of the exchange.
3- Non-custodial (Out of Custody Wallets)
As a second wallet model, Non-custodial (where the wallet keys are in person and used without supervision) models come to the fore. These wallets put the assets and wallets of the users under the patronage of the users. Wallets can be used through private keys left to users.

Wallets, which are left entirely under the control of the crypto user, offer the possibility of decentralization as they are out of surveillance. This model allows users to hide their assets as they wish. The ownership and control of the assets is not provided by any third party. However, the vast majority of these wallets do not yield any profits without staking. The anti-fraud measures of wallets are directly proportional to the users’ own signatures. As long as the user does not approve any transaction, the possibility of being defrauded is reduced to a minimum.