 A group of researchers from New York University have developed DNA-based nanobots that can theoretically replicate themselves exponentially. The tiny DNA robots developed consist of only four DNA strands and can copy themselves one at a time, using their structure as a template. These DNA nanobots can remain inside our bodies and provide a new treatment approach to diseases.
A group of researchers from New York University have developed DNA-based nanobots that can theoretically replicate themselves exponentially. The tiny DNA robots developed consist of only four DNA strands and can copy themselves one at a time, using their structure as a template. These DNA nanobots can remain inside our bodies and provide a new treatment approach to diseases.Self-replicating nanobots
Nanobots created with four DNA strands are approximately 100 nanometers in size. To put this into perspective, you could arrange about a thousand of them side by side, roughly the width of a human hair. They are also kept in a solution containing the specific DNA strand raw materials needed to work.
Nanorobots that can assemble parts into three-dimensional shapes were developed in collaboration with scientists from New York University, Ningbo Cixi Institute of Biomechanical Engineering and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This represents a significant improvement over previous attempts that could only create two-dimensional shapes. New robots use multi-axis precision folding and positioning to reach the third dimension and more degrees of freedom.
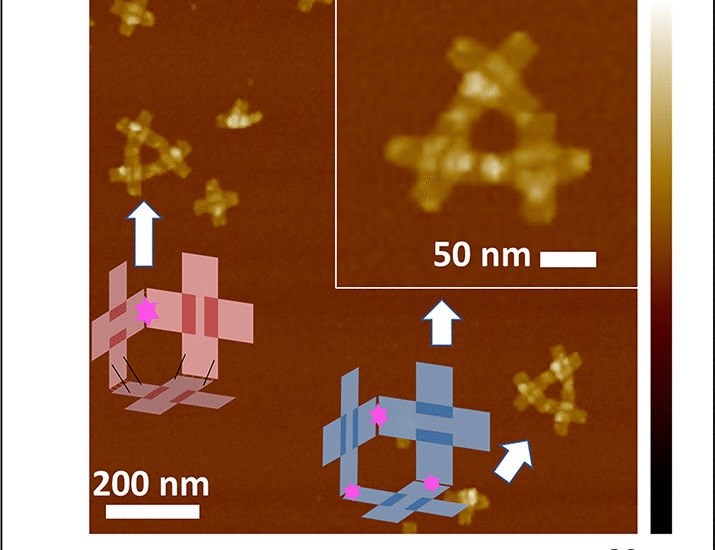 “By utilizing externally controlled temperature and ultraviolet (UV) light, our ~100-nanometer-sized programmable robot grabs the different parts, positions and aligns them so they can be fused, releases the structure, and returns it to its original configuration ready for the next process,” the team wrote in their study published in the journal Science Robotics. “It’s coming back,” he says.
“By utilizing externally controlled temperature and ultraviolet (UV) light, our ~100-nanometer-sized programmable robot grabs the different parts, positions and aligns them so they can be fused, releases the structure, and returns it to its original configuration ready for the next process,” the team wrote in their study published in the journal Science Robotics. “It’s coming back,” he says.Why are nanobots important?
Nanobots like these have the potential to produce drugs, enzymes and other chemicals within body cells. Researchers underline that these machines can copy all 3D structures and functions on their own. Previous research was limited to 2D shapes that had to be converted to 3D shapes, which were at risk of errors. But new research allows creating 3D structures from scratch.
However, it should be noted that DNA nanobots are not completely self-sufficient. The robots move in response to externally controlled temperature and UV light. UV light is needed to weld the pieces of DNA they put together. When those who are sufficiently involved in science fiction culture hear the phrase “self-replicating nanobot”, they may think of the Gray Goo scenario (nanobots that can replicate themselves uncontrollably threaten life). Fortunately, this is unlikely for the DNA nanobots being developed because they have no way of replicating themselves or anything else without sufficient amounts of sensitive DNA fragments and UV light.