 Magnesium ion batteries are a promising battery type developed as a safe, low-cost and high energy density alternative to lithium ion batteries.
Magnesium ion batteries are a promising battery type developed as a safe, low-cost and high energy density alternative to lithium ion batteries.The advantage of magnesium batteries is that they have a higher energy density compared to doped lithium alternatives when used on the anode side. In addition to being safe, stable and low-cost, the fact that magnesium is abundant in nature makes magnesium-ion batteries a promising alternative.
There are two types of magnesium batteries with aqueous and dry electrolytes. Magnesium batteries with dry electrolytes have high energy density, but require high temperatures to maintain their performance. In addition, it poses a safety risk due to its toxicity and flammability. Magnesium batteries with aqueous electrolyte are safer, but have low voltage (1.5V) and energy density due to their narrow electrochemical stability.
Energy density equivalent to lithium-ion batteries
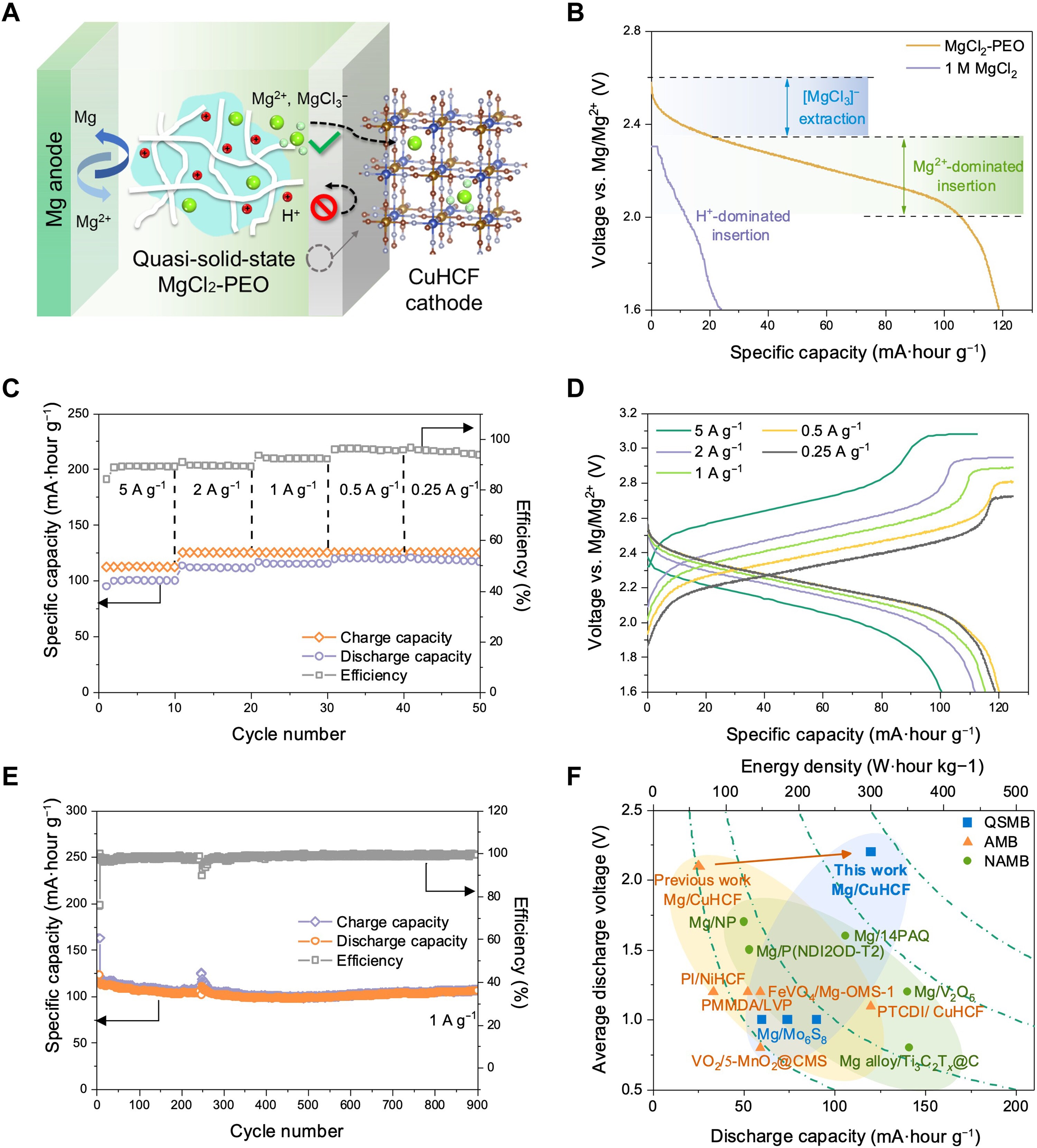
Researchers at the University of Hong Kong adopted a different approach and developed a semi-solid state magnesium ion battery. The battery they developed has a voltage of 2.4 V and an energy density of 264 Wh/kg. These values are much higher than current magnesium ion batteries and are equivalent to lithium ion batteries.
“A game-changing development”
Professor Dennis YC, who is part of the research team, called the battery they developed a “game-changing development” and said, “Our semi-solid state battery combines the best features of both worlds, offering the high voltage of dry systems and the safety and affordability of aqueous systems. This development is based on high-performance magnesium.” “It is a major step forward in the development of ion batteries.” He said his words.
Maintains its capacity even in extreme cold
When the research team tested the battery they developed in extreme cold conditions (-22 degrees), they observed that the battery retained 90% of its capacity even after 900 cycles.
 Associate Professor Wending Pan, one of the research team, said: “The electrolyte development strategy presented in our research has potential extending beyond magnesium ion batteries to other multivalent metal ion batteries such as zinc ion and aluminum ion batteries.” Finally, “We believe that this work will pave the way for next-generation energy storage solutions that are not only efficient but also environmentally friendly.” He said his words.
Associate Professor Wending Pan, one of the research team, said: “The electrolyte development strategy presented in our research has potential extending beyond magnesium ion batteries to other multivalent metal ion batteries such as zinc ion and aluminum ion batteries.” Finally, “We believe that this work will pave the way for next-generation energy storage solutions that are not only efficient but also environmentally friendly.” He said his words.