 Scientists using the European Space Agency’s (ESA) ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) vehicle observed that Mars’ atmosphere glows green in the visible light spectrum for the first time. Interestingly, future Mars explorers may be able to see this bright formation when skies are clear in the planet’s polar regions. Additionally, this naturally bright light could be a useful aid for human vision and rover navigation on dark Martian nights.
Scientists using the European Space Agency’s (ESA) ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) vehicle observed that Mars’ atmosphere glows green in the visible light spectrum for the first time. Interestingly, future Mars explorers may be able to see this bright formation when skies are clear in the planet’s polar regions. Additionally, this naturally bright light could be a useful aid for human vision and rover navigation on dark Martian nights.The sky on Mars turned green
This phenomenon detected on Mars is called airglow (or also known as dayglow or nightglow, depending on the time) and is actually seen on Earth as well. Although at first glance it seems similar to the northern lights (or aurora) on Earth, it is actually a different phenomenon with different causes. According to the ESA, nightglow occurs when two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule. On Mars, this event occurs at an altitude of approximately 50 km. On the other hand, the northern lights generally occur at altitudes of 80 km and above as a result of the collision of charged particles from the Sun with the Earth’s magnetic field.
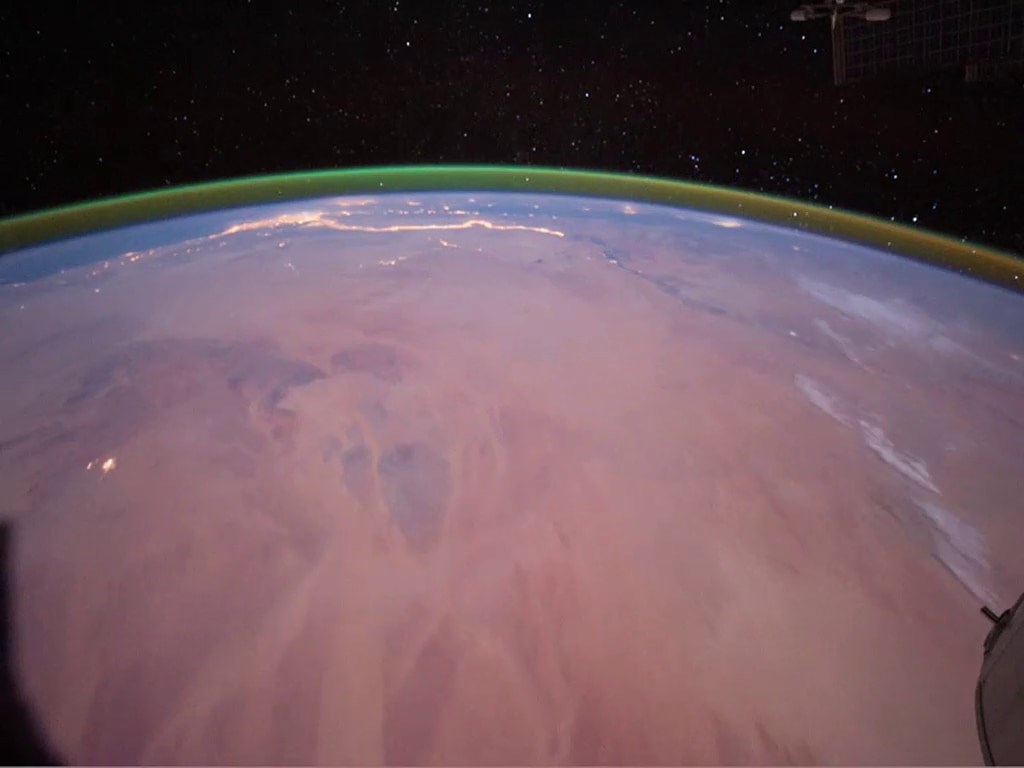 Scientists have suspected airglow on Mars for nearly 40 years, but the first observation was made in the infrared spectrum by ESA’s Mars Express orbiter just a decade ago. Then, in 2020, scientists used TGO to observe the phenomenon in the visible light spectrum in Martian daylight instead of at night. Now, for the first time, it is observed at night and in green color. The image just above shows the airglow phenomenon seen on Earth.
Scientists have suspected airglow on Mars for nearly 40 years, but the first observation was made in the infrared spectrum by ESA’s Mars Express orbiter just a decade ago. Then, in 2020, scientists used TGO to observe the phenomenon in the visible light spectrum in Martian daylight instead of at night. Now, for the first time, it is observed at night and in green color. The image just above shows the airglow phenomenon seen on Earth.Scientists state that knowing the atmospheric parameters of Mars may be useful for future exploration. Studying Mars’ atmosphere could also help design spacecraft that will travel to the Red Planet. A better understanding of the atmosphere’s density could help mission planners build satellites that can withstand the drag created by the Martian atmosphere or design parachutes that can lower payloads to the Red Planet’s surface.